Results - Pervasive Developmental Disorders, including Autism
Children with Pervasive Developmental Disorders, including Autism
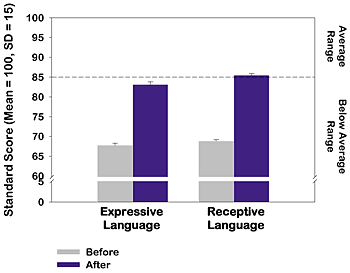
Children diagnosed with Pervasive Developmental Disorders (PDD) made significant gains in their oral language skills after using the Fast ForWord Language program.
One-third of the children were diagnosed with Pervasive Developmental Disorder - Autism, two-thirds were diagnosed with Pervasive Developmental Disorder - not otherwise specified. The improvements seen for the two diagnoses were similar
Improved Language Skills
Methodology
A group of children ranging in age from 5 to 13 years old (with a mean age of 7.95 years) had their oral language skills assessed with the Test of Language Development (TOLD) or the Clinical Evaluation of Language Fundamentals (CELF).
Measures
The CELF is a comprehensive language test widely used to measure a child's ability to understand words and sentences, follow directions, recall and formulate sentences, and understand relationships between words and categories. It is designed for ages 6-21, yet the subtests differ by age.
Overall performance on this test is indicated by a measure called the Total Language Score. It is based upon a combination of the receptive and expressive language measures.
The TOLD is a comprehensive test of language skills used to assess a child's listening, organising, speaking, semantics and syntax skills. It is designed for ages 4-12, yet the subtests differ by age.
The Listening Quotient corresponds to receptive language skills while the Speaking Quotient corresponds to expressive language skills.
Overall performance on this test is indicated by a measure called the Total Language Score. It is based upon a combination of the receptive and expressive language measures.
The TOLD is a comprehensive test of language skills used to assess a child's listening, organising, speaking, semantics and syntax skills. It is designed for ages 4-12, yet the subtests differ by age.
The Listening Quotient corresponds to receptive language skills while the Speaking Quotient corresponds to expressive language skills.
Implementation
The implementation process began with clinicians receiving preliminary training in a number of areas, including:
- Methods for assessing candidates for participation;
- Selection of appropriate standardised language measures for testing and evaluation;
- Effective implementation techniques;
- Proper administration of the products and effective methods for monitoring student progress
Source
Merzenich, M. M., Saunders, G., Jenkins, W. M., Miller, S., Peterson, B. & Tallal, P. (1999). In S. H. Broman & J. M. Fletcher (Eds.), The changing nervous system: Neurobehavioral consequences of early brain disorders. New York: Oxford University Press.