Results - English Language Learners
Improved Phonemic Awareness and Language Comprehension
This nationwide (USA) sample of at-risk students who were English Language Learners significantly improved their phoneme identification skills (foundational reading skills) and their language comprehension (a skill critical for becoming a strong reader).
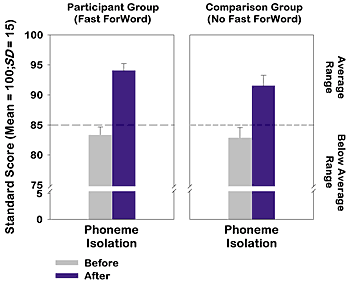
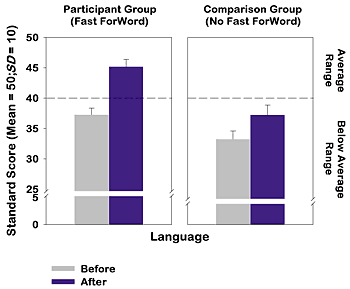
Students who used the Fast ForWord Language program made significantly greater gains in phoneme identification skills than a group of matched control students. The group's language comprehension also moved from below average to well within the average range, showing significantly greater gains than those of the comparison group.
Students who used the Fast ForWord Language program made significantly greater gains in phoneme identification skills than a group of matched control students. The group's language comprehension also moved from below average to well within the average range, showing significantly greater gains than those of the comparison group.
Improved Phonological Awareness
Improved Receptive Language
Methodology
Study participants comprised at-risk students who were English Language Learners from schools throughout USA.. Students were randomly assigned to either use the Fast ForWord Language prgram or to be in a comparison group. Both groups were measured at the start and the end of the study with the Phonological Awareness Test (PAT). and the Test of Auditory Comprehension of Language (TACL), a standardised, nationally normed language test.
Measures
The PAT Isolation subtest assesses the ability to identify phonemes at the beginning, in the middle, and at the end of words. Standard scores on the PAT use a mean of 100 and a standard deviation of 15. With this metric, scores from 85 to 115 are considered in the normal range.
TACL: The Test of Auditory Comprehension of Language measures ability to understand spoken language and comprehend grammar. This test ranks performance relative to a large standardization sample that reflects the gender, age, parent education levels, region and race/ethnicity of the U.S. population. Students with scores between 40 and 60 are deemed to be within the average range
TACL: The Test of Auditory Comprehension of Language measures ability to understand spoken language and comprehend grammar. This test ranks performance relative to a large standardization sample that reflects the gender, age, parent education levels, region and race/ethnicity of the U.S. population. Students with scores between 40 and 60 are deemed to be within the average range
Source
Scientific Learning Corporation (1999) Improved Language Skills by Children with Low Reading Performance who used Fast ForWord Language; MAPS for Learning: Product Report 3(1)1:13